IBM X-Force recently released an excellent report on a new banking trojan named IcedID that is being distributed using computers already infected with Emotet. We took the MD5 of one of the droppers from the IBM report and extracted the payload. After extracting the payload from one of the droppers listed in the report, using Intezer Analyze™, we have found code reuse from another malware named Pony, written about in a report by Proofpoint.
#IcedID banking trojan payload – code overlap with #pony more details soonhttps://t.co/baS1fciJHX@malwrhunterteam @campuscodi
— Jay Rosenberg (@jaytezer) November 13, 2017
Pony is a trojan that was being distributed via the Hancitor downloader, distributed through Microsoft Word documents. The version of Pony used in the reports is believed to be the same threat actor as Vawtrak. It was also sold via underground forums until the source code was leaked online.
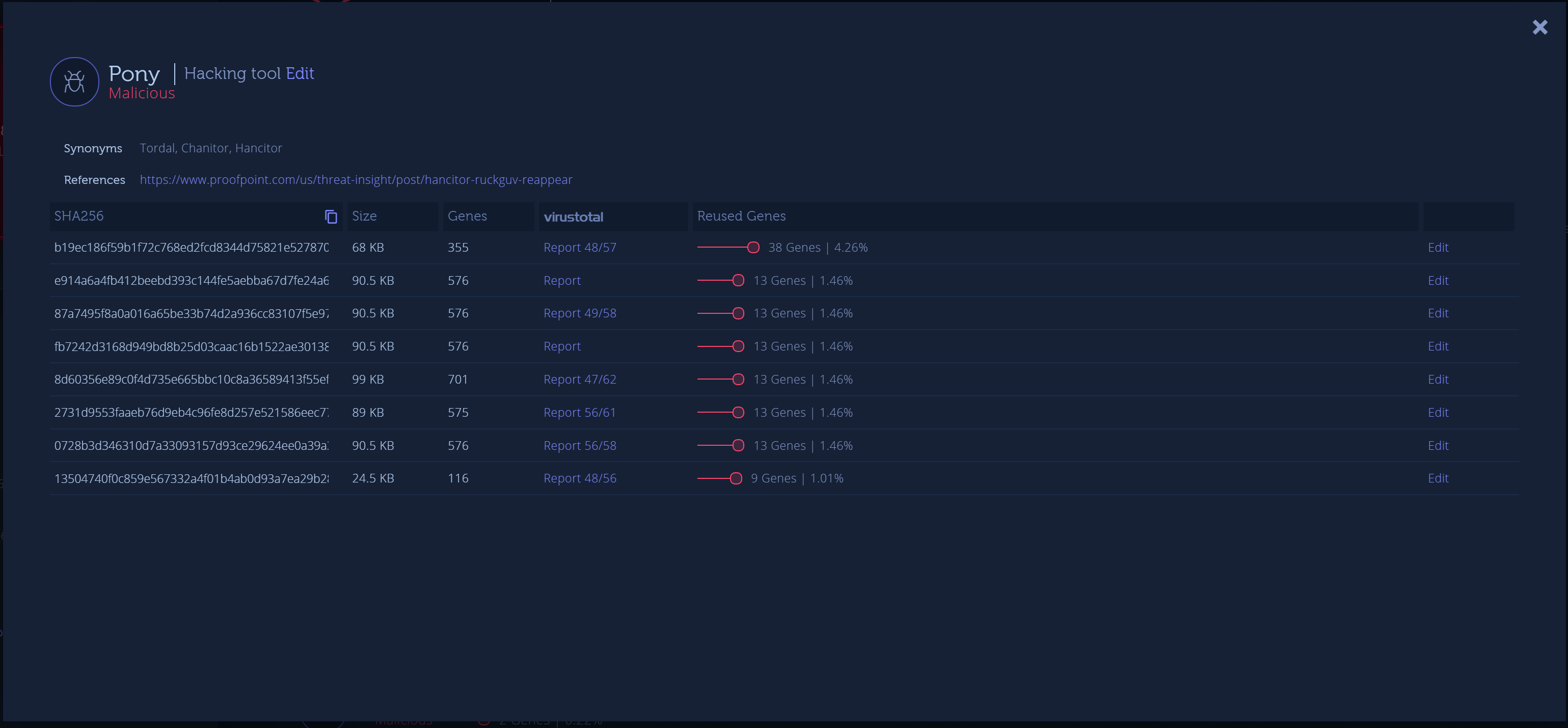
Using the dive-in feature with the related Pony samples, we can see the following:
(Dive-in feature of Intezer Analyze™)
With this information alone, it will be hard to attribute this sample to a certain threat actor due to the public availability of the source code of Pony.
Let’s take a look at some of the matching functions.
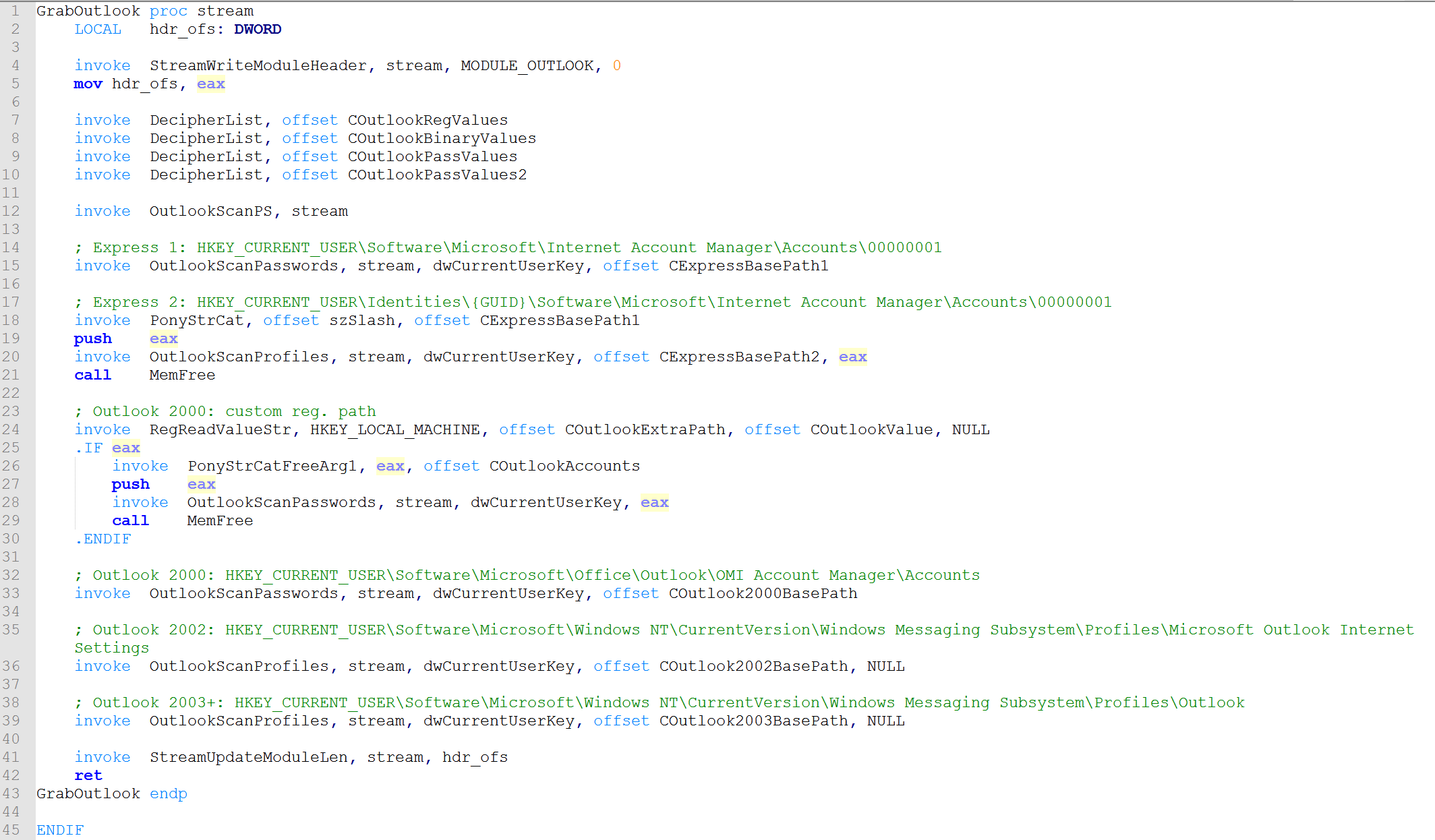
As we can see here, the function in these two samples is a 1:1 match. The function above is called GrabOutlook in the Pony source code and is responsible for stealing passwords from Outlook. (You may notice a difference because the strings appear decrypted in the sample on the left as it looks like Proofpoint dumped the sample with the strings already decrypted before uploading to VirusTotal.)
(GrabOutlook function from Pony 2.0 source code)
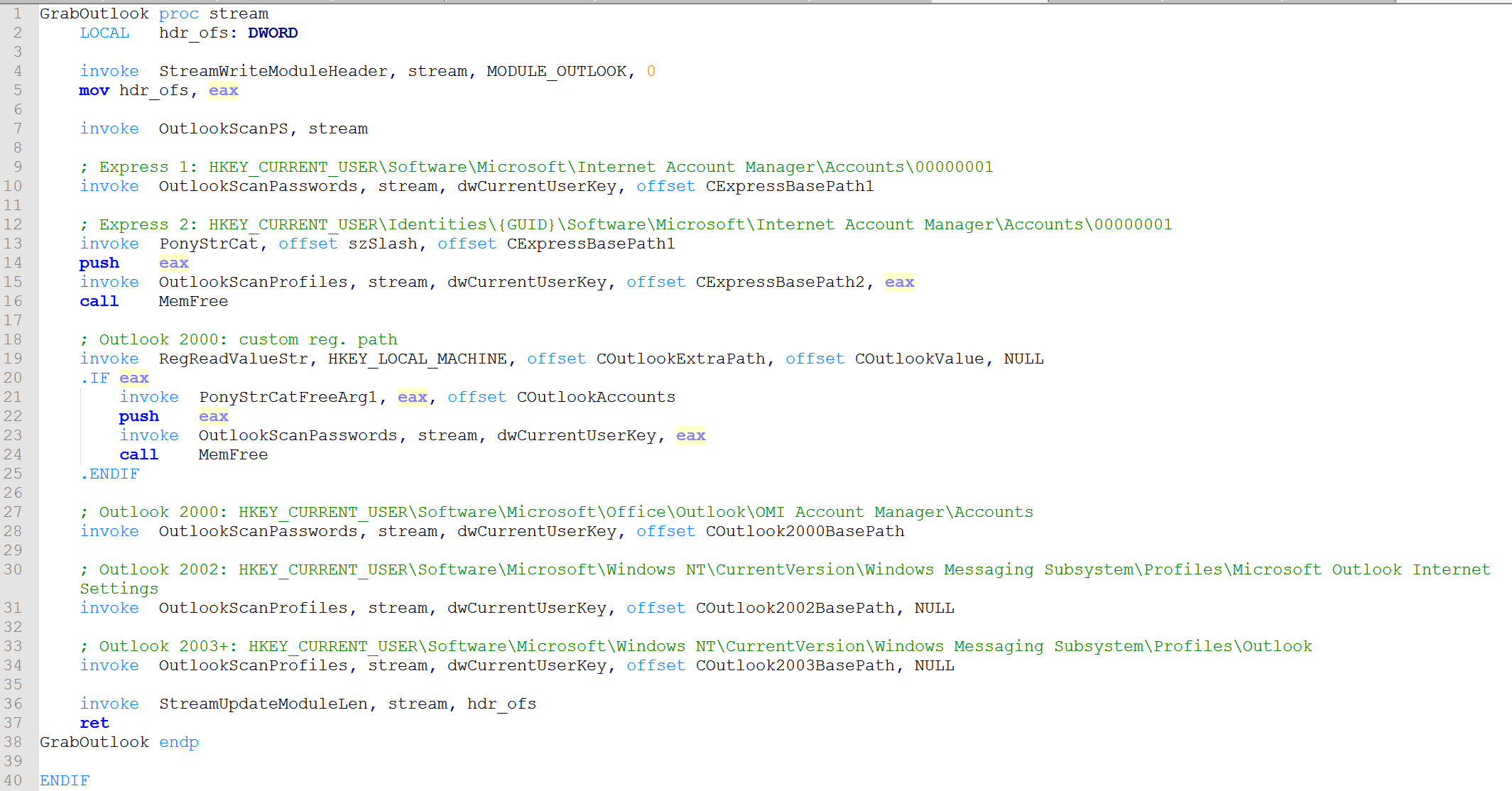
More specifically, we can tell the threat actor used code from version 2.0 of Pony because in the Pony 1.9 source code, we do not see calls to DecipherList which is responsible for decrypting the strings.
(GrabOutlook function from Pony 1.9 source code)
Other shared functions from Pony:
- OutlookExport
- OutlookReadPSItemValue
- OutlookScanPasswords
- OutlookScanProfiles
- PocomailScanReg
- IncrediMailScanReg
- CRC32Update
- CommonCryptUnprotectData
- MapFile
- PonyStrCat
- PonyStrCatFreeArg1
- DecipherList
- UnicodeToAnsiLen
- FileExists
- StreamUpdateModuleLen
- StreamWriteModuleHeader
There may be other functions from Pony, but we can see that the shared code is mostly related to stealing e-mail credentials.
Time and time again, we see threat actors reusing the same code. If we look at reused code, it makes it easier to detect malware. Such small code reuse makes it very difficult to get these kinds of conclusions by manually reverse engineering a file. The ability to automate the finding of code reuse makes our job as malware analysts easier.
Report Samples:
- IcedID Dropper: 29f7469f8dc88820f72a9bdcb02badc1a40aa41b3f4b7f8caaa30409b3842aea
- IcedID Payload: a6531184ea84bb5388d7c76557ff618d59f951c393a797950b2eb3e1d6307013
- Pony: b19ec186f59b1f72c768ed2fcd8344d75821e527870b71e8123db96f683f1b68